This is Part 2 in a series of post dedicated to finding out more information about your DNA test results from 23andMe or Family Tree DNA. If you haven’t read it, yet, view Part 1.
There are four main types of DNA that can be used for genealogy purposes: Autosomal, X Chromosome, Y Chromosome, and Mitochondrial DNA. Each type of DNA is passed down from parents to children in different ways, allowing different patterns or different signs to help in your research. Here is a quick video that I found very useful explaining the four types:
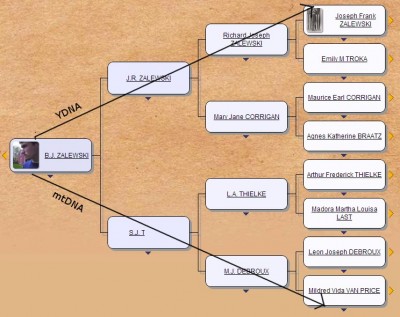
Most people that have taken DNA tests are somewhat familiar with what seem to be the “big two”: Y Chromosome (YDNA) and Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). These are the two types of DNA that literally shoot out in opposite directions from you through your ancestry, though females can only trace mtDNA. They also give you the Haplogroups that you may have seen, one Maternal and one Paternal. Mine are H11a and R1a1a, respectively. They use this to determine where your deep ancestry hails from.
YDNA is passed down from from fathers to sons. The father is the one that determines the sex of a child by either giving an X Chromosome, for female, or a Y Chromosome, for male, which is why only males can use the YDNA information. The YDNA information traces your patrilineal line (or your surname line) back thousands of years since the Y Chromosome does not change very often as it is passed down.
mtDNA is passed down only from mother to all of her children. It works in a similar way to YDNA in that you can use it to trace your matrilineal line back thousands of years (your mother’s mother’s mother and so on.)
Here is another quick video explaining mtDNA. To view a similar video on YDNA, visit the Molecular Genealogy site at the University of Utah as I can’t find a version that I can embed.
View Part 3 for an overview of the X Chromosome and how to determine which ancestors you may get it from.


 In the last week or so I’ve dug deeper into my DNA testing results mainly from my
In the last week or so I’ve dug deeper into my DNA testing results mainly from my 

 My wife,
My wife,